 |
Chicago IL (SPX) Feb 18, 2009 The smallest nano-sized silica particles used in biomedicine and engineering likely won't cause unexpected biological responses due to their size. The result should allay fears that cells and tissues will react unpredictably when exposed to the finest silica nanomaterials in industrial or commercial applications. Nanotoxicologist Brian Thrall and colleagues found that, mostly, size doesn't matter, by using total surface area as a measure of dose, rather than particle mass or number of particles, and observing how cultured cells responded biologically. "If you consider surface area as the dose metric, then you get similar types of responses independent of the size of the particle," said Thrall, a scientist at the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in Richland, Wash. "That suggests the chemistry that drives the biological responses doesn't change when you get down to the smallest nanoparticle." Nanoparticles are materials made up of spherical particles that are on average 100 to 1,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. They are being used in tires, biomedical research, and cosmetics. Researchers are exploring these tiny spheres because their physical and chemical properties at that size offer advantages that standard materials don't, such as being able to float through blood vessels to deliver drugs. But whether these materials are safe for human consumption is not yet clear. Previous work suggested in some cases, nanoparticles become more toxic to cells the smaller the particles get. Thrall presented this toxicology data on amorphous silica nanoparticles at the 2009 American Association for the Advancement of Science's annual meeting. He also presented data on which cellular proteins the nanoparticles use to get inside cells. One difficulty in measuring toxicity is that not everyone agrees which kind of dose unit to compare. Some researchers measure the dose by total weight, some by the number of particles. Neither method distinguishes whether a nanomaterial's toxicity is due to the inherent nature of the material or the particle size under scrutiny. "Different dose metrics give different impressions of which particles are more toxic," he said. To find out, Thrall and his colleagues at PNNL measured the dose at which the particles caused a biological response. The biological response was either death of the cell, or a change in which genes the cell turned on and off. They found that when calculating doses by particle number or mass, the amount needed to generate a biological response was all over the map. They found that the best way to pinpoint how toxic the particles are to cells was to calculate the dose based on the total surface area of the nanomaterial. Only when they considered the surface area of the dose could they predict the biological response. And the biological response, they found, was very similar regardless of the size of the nanoparticles. Inside cells, some genes responded to nanoparticles by ramping up or down. More than 76 percent of these genes behaved the same for all nanoparticle sizes tested. This indicated to the researchers that, for these genes, the nanoparticles didn't pick up weird chemical properties as they shrunk in size. "The big fear is that you'd see unique biological pathways being affected when you get down to the nanoscale. For the most part, we didn't see that," said Thrall. However, the team found some genes for which size did matter. A handful of genes, these fell into two categories: smaller particles appeared to affect genes that might be involved in inflammation. The larger particles appeared to affect genes that transport positively charged atoms into cells. This latter result could be due to metals contaminating the preparation of the larger particles, Thrall suggested. Overall, the results contribute to a better understanding of what goes on at the nanoscale. Related Links DOE/Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Nano Technology News From SpaceMart.com Computer Chip Architecture, Technology and Manufacture
 Davis CA (SPX) Feb 02, 2009
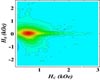
Davis CA (SPX) Feb 02, 2009In the race to develop the next generation of storage and recording media, a major hurdle has been the difficulty of studying the tiny magnetic structures that will serve as their building blocks. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright Space.TV Corporation. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space.TV Corp on any Web page published or hosted by Space.TV Corp. Privacy Statement |