 |
Madison WI (SPX) Dec 17, 2010 The manufacturing of nanomaterials has been steadily on the rise in the medical, industrial, and scientific fields. Nanomaterials are materials that are engineered to have dimensions less than 100 nanometers and have very unique properties as a result of their small size. In a study funded by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, a team of scientists from the University of Kentucky determined that earthworms could absorb copper nanoparticles present in soil. One crucial step in determining the uptake of nanomaterials was discerning whether uptake of metal ions was released from the nanomaterials or the nanomaterials themselves. Using x-ray analysis, researchers were able to differentiate between copper ions and copper nanoparticles by examining the oxidation state of copper in the earthworm tissues. Many products will release their nanomaterials either as a result of regular use or after disposal. These discarded nanoparticles could enter waterways and eventually soil. According to the authors, it is unclear how nanomaterials interact in the environment due to lack of scientific research; however, there is a possibility of unintentional ingestion by humans and animals. Jason Unrine, the lead author of the study said, "This was one of the first studies to demonstrate that engineered nanomaterials can be taken up from the soil by soil organisms and enter food chains, and it has significant implications in terms of potential exposure to nanomaterials for both humans and ecological receptor species." Unrine assures that ongoing studies are being conducted on transformation, bioavailability, trophic transfer, and adverse effects of engineered nanomaterials in terrestrial ecosystems. Nanomaterials are used in a variety of instruments and consumer goods including protective coatings and solar cells.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links American Society of Agronomy (ASA) Nano Technology News From SpaceMart.com Computer Chip Architecture, Technology and Manufacture
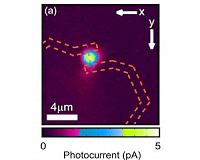 Single Quantum Dot Nanowire Photodetectors
Single Quantum Dot Nanowire PhotodetectorsWashington DC (SPX) Dec 16, 2010 Moving a step closer toward quantum computing, a research team in the Netherlands recently fabricated a photodetector based on a single nanowire, in which the active element is a single quantum dot with a volume of a mere 7,000 cubic nanometers. The device is described in the American Institute of Physics' journal Applied Physics Letters. Photodetectors based on single quantum dots a ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |