 |
Greenbelt MD (SPX) Jan 20, 2011 A wider range of asteroids were capable of creating the kind of amino acids used by life on Earth, according to new NASA research. Amino acids are used to build proteins, which are used by life to make structures like hair and nails, and to speed up or regulate chemical reactions. Amino acids come in two varieties that are mirror images of each other, like your hands. Life on Earth uses the left-handed kind exclusively. Since life based on right-handed amino acids would presumably work fine, scientists are trying to find out why Earth-based life favored left-handed amino acids. In March, 2009, researchers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., reported the discovery of an excess of the left-handed form of the amino acid isovaline in samples of meteorites that came from carbon-rich asteroids. This suggests that perhaps left-handed life got its start in space, where conditions in asteroids favored the creation of left-handed amino acids. Meteorite impacts could have supplied this material, enriched in left-handed molecules, to Earth. The bias toward left-handedness would have been perpetuated as this material was incorporated into emerging life. In the new research, the team reports finding excess left-handed isovaline (L-isovaline) in a much wider variety of carbon-rich meteorites. "This tells us our initial discovery wasn't a fluke; that there really was something going on in the asteroids where these meteorites came from that favors the creation of left-handed amino acids," says Dr. Daniel Glavin of NASA Goddard. Glavin is lead author of a paper about this research published online in Meteoritics and Planetary Science January 17. "This research builds on over a decade of work on excesses of left-handed isovaline in carbon-rich meteorites," said Dr. Jason Dworkin of NASA Goddard, a co-author on the paper. "Initially, John Cronin and Sandra Pizzarello of Arizona State University showed a small but significant excess of L-isovaline in two CM2 meteorites. Last year we showed that L-isovaline excesses appear to track with the history of hot water on the asteroid from which the meteorites came. In this work we have studied some exceptionally rare meteorites which witnessed large amounts of water on the asteroid. We were gratified that the meteorites in this study corroborate our hypothesis," explained Dworkin. L-isovaline excesses in these additional water-altered type 1 meteorites (i.e. CM1 and CR1) suggest that extra left-handed amino acids in water-altered meteorites are much more common than previously thought, according to Glavin. Now the question is what process creates extra left-handed amino acids. There are several options, and it will take more research to identify the specific reaction, according to the team. However, "liquid water seems to be the key," notes Glavin. "We can tell how much these asteroids were altered by liquid water by analyzing the minerals their meteorites contain. The more these asteroids were altered, the greater the excess L-isovaline we found. This indicates some process involving liquid water favors the creation of left-handed amino acids." Another clue comes from the total amount of isovaline found in each meteorite. "In the meteorites with the largest left-handed excess, we find about 1,000 times less isovaline than in meteorites with a small or non-detectable left-handed excess. This tells us that to get the excess, you need to use up or destroy the amino acid, so the process is a double-edged sword," says Glavin. Whatever it may be, the water-alteration process only amplifies a small existing left-handed excess, it does not create the bias, according to Glavin. Something in the pre-solar nebula (a vast cloud of gas and dust from which our solar system, and probably many others, were born) created a small initial bias toward L-isovaline and presumably many other left-handed amino acids as well. One possibility is radiation. Space is filled with objects like massive stars, neutron stars, and black holes, just to name a few, that produce many kinds of radiation. It's possible that the radiation encountered by our solar system in its youth made left-handed amino acids slightly more likely to be created, or right-handed amino acids a bit more likely to be destroyed, according to Glavin. It's also possible that other young solar systems encountered different radiation that favored right-handed amino acids. If life emerged in one of these solar systems, perhaps the bias toward right-handed amino acids would be built in just as it may have been for left-handed amino acids here, according to Glavin. The research was funded by the NASA Astrobiology Institute (NAI), which is administered by NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif.; the NASA Cosmochemistry program, the Goddard Center for Astrobiology, and the NASA Post Doctoral Fellowship program. The team includes Glavin, Dworkin, Dr. Michael Callahan, and Dr. Jamie Elsila of NASA Goddard.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Goddard Space Flight Center Asteroid and Comet Mission News, Science and Technology
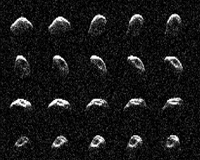 NASA Radar Reveals Features on Asteroid
NASA Radar Reveals Features on AsteroidPasadena CA (JPL) Jan 13, 2011 Radar imaging at NASA's Goldstone Solar System Radar in the California desert on Dec. 11 and 12, 2010, revealed defining characteristics of recently discovered asteroid 2010 JL33. The images have been made into a short movie that shows the celestial object's rotation and shape. A team led by Marina Brozovic, a scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., made the disc ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |