 |
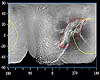
Bonn, Germany (SPX) May 29, 2008 Like the cartographers of old, scientists working with images from the Cassini spacecraft of Saturn's icy airless moons have carefully crafted detailed maps that one day may guide future explorers across the surfaces of these remote bodies. A team of DLR scientists alongside colleagues from the Freie Universit�t Berlin has produced an atlas of Dione, a moon of Saturn. In charting the fractured 1125-km-wide moon Dione, the Cassini Imaging Team is releasing the third in its series of atlases of Saturn's icy satellites. The team has previously released atlases of geologically active Enceladus and the obscure outer moon Phoebe. Atlases of other moons will be released as Cassini's mission continues. Iapetus and Tethys are next in line.
Combining 449 images into one atlas "We then cut the map into 15 pieces, with each piece forming a section of the atlas," he said. Each of the 15 pieces is produced at a scale of 1:1,000,000: that is, where 1 centimetre on the map is 10 000 kilometres on the surface of Dione. Along with the 15 smaller maps, the single global map created by Roatsch and the DLR cartographers is also being released today. This map adds to Cassini's growing collection of similar views of Saturn's icy denizens. It is important for planetary scientists to have precise maps of the worlds they study and the Cassini atlases are a major step toward characterising the large icy satellites of Saturn. They will serve as the basis for geologic interpretations, estimates of the ages of surface regions, and deciphering the processes that formed the moons' landscapes. But most importantly, with their precise reckoning in latitude and longitude, these maps allow scientists to easily find, and refer to, features of interest on the moon's surface.
Good mapping lays the ground for future research of the icy moon Thus far in Cassini's mission, the north polar regions of Dione and the other moons of Saturn (as well as the planet itself) have remained shrouded in seasonal darkness. Saturn takes nearly 30 years to orbit the Sun, and its seasons are more than seven years long. "Fortunately we were able to combine our Cassini data with lower-resolution images taken by the Voyager spacecraft in 1981," said Roatsch. As the Cassini mission continues, higher northern latitudes will come into sunlight, and Cassini maps should continue to improve. Naming features on these moons is another necessary but pleasant task, according to Roatsch. On all satellites of the four gas-giant planets, the craters, plains, ridges and troughs are named after people and places from ancient mythologies of various cultures. Features on Dione draw names from Virgil's "Aeneid." The Cassini Imaging Team proposed 45 new names for geological features on Dione, and these were recently approved by the International Astronomical Union, which oversees the naming and classification of celestial bodies. "Cassini's exploration of these bodies leaves a glorious and important legacy for generations to come", said,Carolyn Porco, Cassini imaging team leader and director of the Cassini Imaging Central Laboratory for Operations (CICLOPS) at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado. "Both robotic and human travelers to Saturn in the future will surely rely on this growing collection of maps and their derivatives to find their way among the moons of Saturn." The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging team consists of scientists from the US, UK, France and Germany. The imaging operations centre and team leader (Dr C. Porco) are based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado, USA. Related Links Explore The Ring World of Saturn and her moons Jupiter and its Moons The million outer planets of a star called Sol News Flash at Mercury
 Boulder CO (SPX) May 22, 2008
Boulder CO (SPX) May 22, 2008Like the ancient cartographers of old, scientists working with images from NASA's Cassini spacecraft of Saturn's icy, airless moons have carefully crafted detailed maps that one day may guide future explorers across the surfaces of these remote bodies. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright Space.TV Corporation. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space.TV Corp on any Web page published or hosted by Space.TV Corp. Privacy Statement |